¶ Understanding the Expanded Version of UTxO in Cardano in a Simple Way
Abstract
> The (e)UTxO (Extended Unspent Transaction Output) model in Cardano enhances the traditional UTxO system by allowing more complex transactions, such as smart contracts. Unlike the basic UTxO model, which tracks the movement of assets as simple outputs from transactions, (e)UTxO can carry additional data (datum) and scripts, enabling the execution of smart contracts and supporting multi-assets. This model maintains the benefits of UTxO, such as security and transparency, while adding flexibility for developers to create more sophisticated applications on the Cardano blockchain. {.is-info}1. What is Cardano?
Cardano is a blockchain that focuses on being secure and flexible. It was made using science and research. Its main goals are to be sustainable, work reliably, and be clear about how it works. Cardano is open to everyone and wants to help people worldwide, especially those without bank services. It uses a special computer language to make sure it is very secure. Cardano is also creating a system for smart contracts, which are agreements that work automatically, to support new kinds of apps and to keep improving over time.¶ 1.1 Cardano's ADA
Digital currency: ADA is Cardano's digital money. Like other digital currencies, you can buy, sell, and exchange ADA. It serves as a way to keep value and helps with fast, cheap money transfers, similar to other digital currencies.
Fuel for operations: ADA is needed to run things on Cardano's network. For example, to use a smart contract on Cardano, you pay with ADA. This use of ADA as 'fuel' helps keep the network running by encouraging those involved to process transactions and confirm blocks.
¶ 1.2 Cardano’s Vision
Bringing change: Cardano wants to make a difference in the real world. Its aim is to give financial services to those who don't have bank accounts, make voting more secure, and develop ways for people to safely keep their personal information.
¶ 1.3 The Community and Governance
Decentralization: Cardano aims for no single person or group to control it. It does this through a special way of making decisions, where people who own ADA can help decide its future. An important part of this are ADA staking pools, which help spread out the power of managing transactions and creating new blocks, so no one person or group is in charge. There are over 3,000 of these pools helping to keep Cardano running smoothly and securely. Please see our article "How to participate in Blockchain Governance " to learn more about governance and decentralized decision making.
Open participation: Anyone with ADA can help make decisions for Cardano. This means everyone has a chance to share their opinion. ADA owners can vote on changes or offer their ADA to a staking pool, or even start their own pool. This is not just for earning rewards but also plays a big role in how Cardano is run, as it affects which pools get to create blocks and have a say in the network.
Understanding ADA staking pools in Cardano shows us the blockchain is about building a fair digital world for all, not just technology. With many staking pools and chances for ADA owners to join, Cardano shows its dedication to shared control and people-powered governance. For more about staking, see "How staking works"
2. The (e)UTxO model
¶ 2.1 What is the (e)UTxO Model?
The (e)UTxO model in Cardano, inspired by Bitcoin's reliable UTxO system which has worked well for over a decade, introduces improvements. It keeps Bitcoins strengths in handling transactions securely and efficiently but adds the ability to include more data in transactions, like smart contracts. This makes Cardano's blockchain more versatile, allowing for complex transactions and applications, while maintaining high security and performance standards.
The model also offers flexibility in transaction conditions, expanding the types of applications that can be developed on Cardano, especially those needing detailed transaction logic.
¶ 2.2 Why is (e)UTxO Important?
-
More than just storing money
In Cardano, the (e)UTxO model doesn't just keep track of how much digital currency someone has. It also stores rules about how that money can be spent. This is especially useful for things like smart contracts. -
Security and efficiency
The (e)UTxO model stands out for its security, ensuring transactions comply with set rules, and efficiency, by processing multiple transactions simultaneously. Moreover, its underlying UTxO mode has a proven track record as the longest tested account model as it is utilized by Bitcoin for over a decade without issues. -
Determinism
Determinism in handling transactions and scripts means everything is predictable. This ensures a user knows in advance how their transaction will affect the blockchains state, avoiding surprises like failed script validations, unexpected fees or unanticipated changes in the ledger or script states.
3 Technical Aspects of the (e)UTxO Model
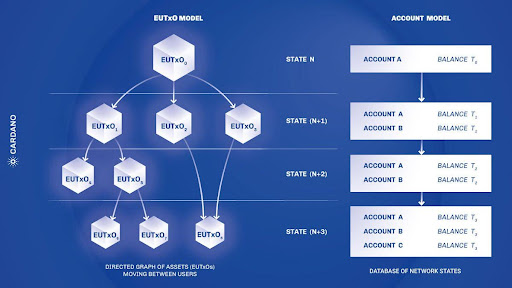
Cardano employs the extended Unspent Transaction Output ((e)UTxO) accounting framework, which is distinct from Ethereums account-based system. In the Ethereum model, each user maintains an account that holds a balance. As funds are transferred between accounts, these balances are accordingly adjusted.
-
Transaction outputs as piggy banks: Imagine every transaction on Cardano creates a virtual piggy bank. Each piggy bank has a certain amount of Cardano's currency, ADA, and rules about how that ADA can be spent.
-
"Extended" part: The 'Extended' in (e)UTxO means that these piggy banks can hold more than just ADA; they can also contain special instructions or conditions. This is like having a piggy bank that not only holds coins but also has a note attached saying under what conditions the coins can be used.
The "e" in (e)UTxO signifies "extended," enhancing the Unspent Transaction Output (UTxO) model. Unlike UTxO smart contracts, which only engage with direct requests to verify a transaction, the (e)UTxO model in Cardano offers advancements beyond this basic functionality.
¶ 3.1 The (e)UTxO model integrates the following transaction mechanisms:
The (e)UTxO model is a bit like a sophisticated way of tracking who owns what on the Cardano blockchain.
Let's break it down:
¶ 3.2 How (e)UTxO Works
-
Creating transaction outputs
When someone sends ADA, they essentially create these piggy banks (transaction outputs) for the receiver. -
Spending ADA
To spend ADA from a piggy bank, the receiver needs to meet the conditions attached to it. This could be something like providing a digital signature to prove they are the rightful owner. -
Unspent outputs
Any ADA in these piggy banks that hasn't been used yet is what we call "Unspent Transaction Output" or UTXO. The 'Extended' part in (e)UTxO means these unspent outputs can do more complex things because of the extra information they hold.
¶ 3.3 Benefits of (e)UTxO
Security: It's secure because every transaction is clearly tracked and conditions must be met to spend the ADA, reducing the chances of fraud.
Versatility: It's versatile as it allows for more complex transactions, like those needed for smart contracts (automated digital contracts).
¶ 3.4 (e)UTxO in Simple Transactions
Simple example: Imagine Alice sends 10 ADA to Bob. In the (e)UTxO model, this transaction would create a new piggy bank with 10 ADA that Bob can now spend. But, if there are special conditions attached to this ADA, Bob will need to meet them to use this money.
A detailed walkthrough can be found in this video by IOG Academy.
¶ 3.5 (e)UTxO in Smart Contracts
Smart contracts: These are like automated agreements. With (e)UTxO, these contracts can be more complex, involving various conditions and rules that must be met for the transaction to go through.
In essence, the (e)UTxO model in Cardano allows for both simple and complex transactions by creating these piggy banks (UTxOs) with specific rules for spending, ensuring security and enabling numerous functionalities on the blockchain.
4. Why and How Cardano Created the (e)UTxO Model - Explained Simply
Understanding the creation of the (e)UTxO model in Cardano might seem complicated, but let's simplify it:
¶ 4.1 Reasons for Development
-
Making Bitcoins UTxO model better
Imagine Bitcoins UTxO model as a wallet where you keep all your different notes and coins. Cardano wanted to improve on this concept. -
Adding Ethereum smart contract features
Ethereum uses a system similar to a bank account for its transactions and smart contracts. Cardano's goal was to combine Bitcoin's straightforward approach with the advanced features of Ethereum’s smart contracts. It's worth noting that Ethereum’s model might appear simpler than the UTxO model, suggesting that perhaps more detail is needed to explain why this might not always be the case. -
Solving existing problems
The traditional UTxO model and the account-based model both have their drawbacks, such as dealing with complex transactions or scaling the system efficiently. The (e)UTxO model was designed to address these issues.
¶ 4.2 Basic Ideas Behind the (e)UTxO Model
-
Keeping things secure and easy
A major idea behind the (e)UTxO model is to make sure it stays as secure and straightforward as the traditional UTXO model, kind of like keeping a wallet system both easy to understand and safe. -
Improving smart contracts
The (e)UTxO model also aims to allow for more complicated transactions, especially with smart contracts. Think of it as programming your wallet to take care of payments automatically when certain conditions are met – that's what (e)UTxO offers. -
Being predictable and efficient
Another focus of the (e)UTxO model is to ensure transactions are done predictably and the system works smoothly, even with lots of transactions happening.
In short, Cardanos (e)UTxO model was created to take the best parts of other blockchain systems while fixing their issues. Its main goals include keeping the system secure, making transactions for smart contracts better, and ensuring everything runs efficiently and predictably.
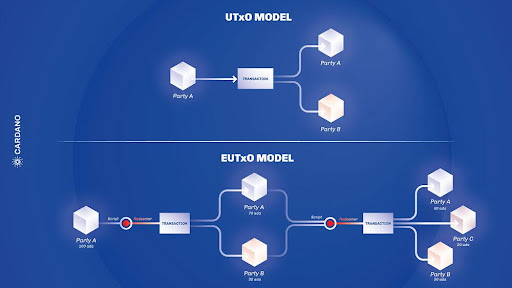
5. Comparison with Traditional UTXO Model
Let's compare Cardanos (e)UTxO model with the traditional UTXO model used in blockchains like Bitcoin to understand their differences in simpler terms.
The infographic below, created by IOG, shows a comparison between the two models:
¶ 5.1 Traditional UTXO model (example)
Like getting exact change: Think of the traditional UTxO model as getting change from a cash transaction. For example, if you buy something for $5 and pay with a $10 bill, you get $5 back as change.
In Bitcoin, when you make a transaction, the 'change' comes back to you as a new UTxO, representing your remaining balance.
Simple and secure: This model is straightforward and secure because it tracks each piece of currency (like each dollar bill) as it moves through transactions.
¶ 5.2 Understanding the (e)UTxO Model in Cardano
Adding extra details
Think of the (e)UTxO model as an upgrade to the traditional UTxO system. It's similar to receiving your change with a small note on each bill, specifying how you can use it in the future. This 'note' adds extra rules or details about the transaction.
Enabling smart contracts
With these additional details, the (e)UTxO model lets Cardano manage smart contracts. Imagine money that knows when and how to spend itself based on predefined rules.
¶ 5.3 Exploring the Key Differences and Benefits of the (e)UTxO Model
-
Handling more complex transactions
The traditional UTxO model is good for straightforward transactions, but the (e)UTxO model steps it up. It can deal with more complicated transactions because it includes extra information. -
Better scalability
The (e)UTxO model is better at handling lots of transactions at once, which helps the network grow and manage more actions smoothly. -
Improved security
While both models are secure, the (e)UTxO model adds extra layers of rules and conditions, giving you more control and making transactions safer. -
More versatile
For those building decentralized apps, the (e)UTxO model is more versatile, allowing for many different kinds of transactions.
In short, Cardano's (e)UTxO model improves on the traditional UTXO model by keeping its straightforwardness and security but adds the capability for more complex, rule-guided transactions. This makes it more adaptable for various uses in the blockchain space.
6. Practical Uses of the (e)UTxO Model in Cardano
The (e)UTxO model in Cardano isn't just theory; it's a practical tool that opens up new possibilities in blockchain technology. Here's how it works in everyday applications, explained simply.
-
Smart contracts:
self-running digital contracts
Think of smart contracts as automatic contracts with the rules coded right in. With the (e)UTxO model in Cardano, these contracts can follow more detailed rules and conditions. -
Example:
It's like a high-tech vending machine that not only gives you a drink for the right amount of money but can also do more complicated deals, like only selling on certain days or to certain people. -
Financial transactions:
safe and fast money moves
The (e)UTxO model helps make sending money on Cardano both safe and fast, kind of like a super-secure digital mailing system where every package (your money) travels exactly where it should, following strict guidelines. -
Benefit:
This reduces mistakes and scams, offering a trustworthy way to move digital money around. -
Decentralized finance (DeFi):
banking without the bank
DeFi lets you do banking stuff - like lending, borrowing, and investing - without an actual bank. The (e)UTxO model supports these services, ensuring they're safe and adaptable. -
Impact:
This way, even people who can't use regular banks can get financial services, making finance more available to everyone. -
Tokenization and NFTs:
making digital things you can own
Tokenization means turning real assets into digital tokens. This includes NFTs, or unique digital items like artwork. The (e)UTxO model lets people create, buy, sell, and trade these digital items safely. -
Real-world example:
Artists can sell their digital art as NFTs, and buyers can own these pieces confidently on the Cardano blockchain, thanks to the (e)UTxO model.
Unlike some platforms where managing tokens requires smart contracts, Cardano lets you issue tokens directly. This is a big deal because it simplifies creating and handling digital assets.
By making these applications possible, the (e)UTxO model helps Cardano make blockchain technology more practical and valuable for all sorts of digital finance and asset management.
7. Challenges and Drawbacks of the (e)UTxO Model
Even though the (e)UTxO model in Cardano brings a lot of benefits, like any technology, it has its own challenges and limitations. Let's break these down into simpler terms:
¶ 7.1 Complexity for Developers
More difficult to create apps
Imagine the (e)UTxO model as a high-tech smartphone with lots of features. While it can do more, it's also trickier to use. For those building apps on Cardano, this means facing more complexity due to the extra rules and data the (e)UTxO model includes.
Steep learning curve
For developers new to this system, especially those from simpler backgrounds, starting to build on Cardano can be daunting.
¶ 7.2 Scalability Concerns
Dealing with lots of activity
Picture a road jam-packed with cars leading to slow-moving traffic. In the same way, the (e)UTxO model, despite being effective, might struggle when too many transactions are happening all at once, potentially causing delays or higher costs to process these transactions.
Finding the right balance
As more complex contracts are used and the network expands, it can be tough to keep the system both complex enough to do what's needed and efficient enough to handle a lot of transactions.
¶ 7.3 User Experience Issues
Making it easy for everyone
The (e)UTxO model's complexity isn't just a hurdle for developers; ordinary users might also find it challenging to grasp how things work on Cardano, making the platform less user-friendly, especially for blockchain newcomers.
While there are hurdles, it's crucial to remember that the (e)UTxO model marks a significant advancement in blockchain tech. It's designed for better security and flexibility, suitable for numerous uses. As with any tech, tackling these limitations often paves the way for more innovation and progress.
¶ 8. Wrapping up Cardano's (e)UTxO Model: A Fusion of Innovation and Flexibility in Blockchain Technology
Cardano's Extended Unspent Transaction Output ((e)UTxO) model is an advanced version of the traditional UTxO system, integrating complex data and rules within transactions. This enhancement allows for smart contracts to be directly embedded in transactions, facilitating not only the transfer of value but also the execution of specific instructions under defined conditions. It maintains the advantages of the original UTxO model, such as predictability and the ability to process transactions in parallel, while also introducing the capability to support intricate decentralized applications. Despite its complexity and the challenges it presents in managing numerous transactions simultaneously, the (e)UTxO model represents a significant progress in blockchain technology. It enhances security, increases the capacity for activity, and demonstrates Cardano's commitment to expanding the utility of blockchain beyond mere digital currency, towards a diverse ecosystem of decentralized applications and services.
List of Figures
compare (https://forum.cardano.org/t/brief-introduction-to-cardanos-eutxo-accounting-model/100893)
compare ((https://www.essentialcardano.io/infographic/eutxo-v-account-based-models)
EUtxO Model vs Account Model (https://global.discourse-cdn.com/business4/uploads/cardano/optimized/3X/2/0/206e4f51eb92a1bf3534247e18b378f40495f213_2_1000x562.jpeg) ↩︎
EUtxO vs UTxO Model (https://global.discourse-cdn.com/business4/uploads/cardano/optimized/3X/a/9/a9af3c665177df48ab5ed3b249b466db82dc59b7_2_1000x562.jpeg) ↩︎
EUTxO Components (https://global.discourse-cdn.com/business4/uploads/cardano/optimized/3X/b/3/b3351160eb9145c7cfc6a3cf80171547f09a8318_2_1000x533.jpeg) ↩︎
Infographic Eutxo v. account-based-models (https://www.essentialcardano.io/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fucarecdn.com%2F466e4cd4-7871-4fe9-a6c0-8dd66f06e0cc%2F&w=3840&q=75) ↩︎